Senior Test Automation Engineer Interview Scorecard
TL;DR
A focused interview scorecard to evaluate Senior Test Automation Engineers on technical craft, system integration, and team impact. It helps interviewers consistently rate candidates against observable behaviors tied to production-quality automation and collaboration.
Who this scorecard is for
Designed for hiring managers, tech leads, and senior recruiters evaluating mid-to-senior level automation engineers. Useful for interview panels assessing coding, framework design, CI/CD integration, problem solving, and mentorship ability.
Preview the Scorecard
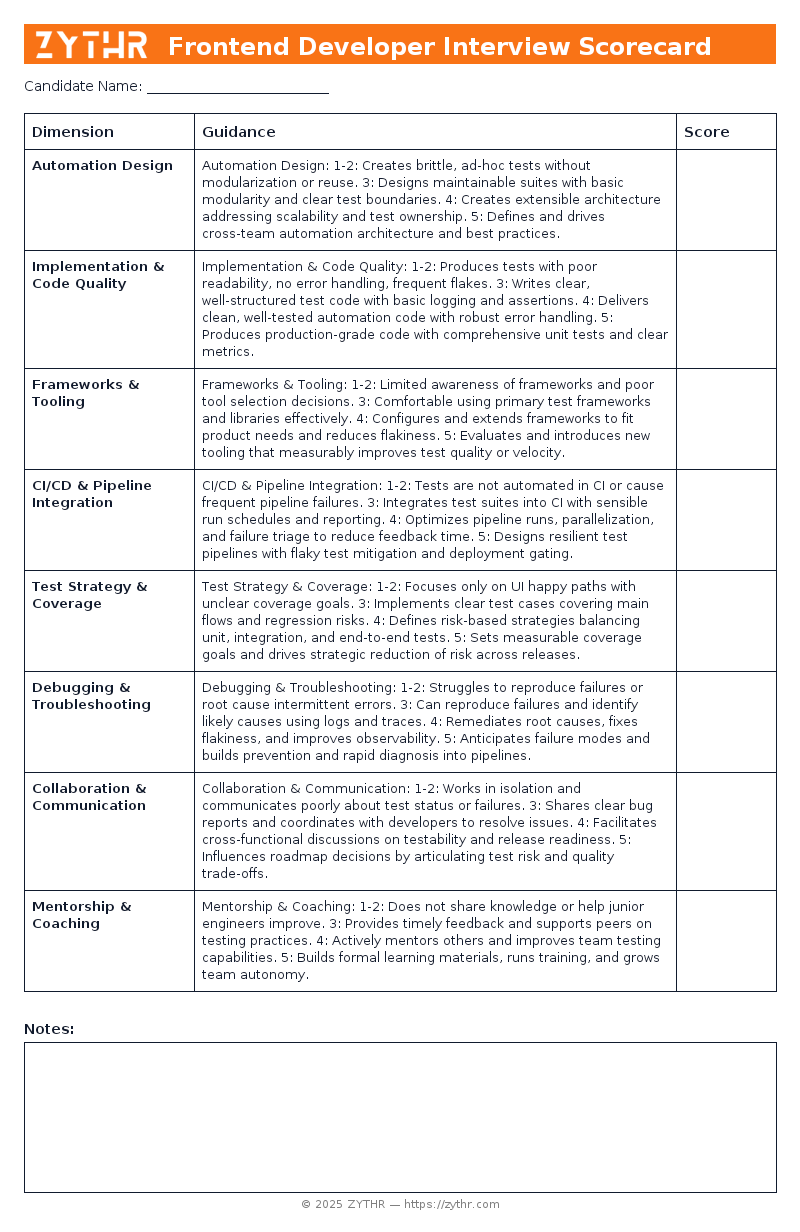
See what the Senior Test Automation Engineer Interview Scorecard looks like before you download it.
How to use and calibrate
- Pick the level (Junior, Mid, Senior, or Staff) and adjust anchor examples accordingly.
- Use the quick checklist during the call; fill the rubric within 30 minutes after.
- Or use ZYTHR to transcribe the interview and automatically fill in the scorecard live.
- Run monthly calibration with sample candidate answers to align expectations.
- Average across interviewers; avoid single-signal decisions.
Detailed rubric with anchor behaviors
Automation Design
- 1–2: Creates brittle, ad-hoc tests without modularization or reuse.
- 3: Designs maintainable suites with basic modularity and clear test boundaries.
- 4: Creates extensible architecture addressing scalability and test ownership.
- 5: Defines and drives cross-team automation architecture and best practices.
Implementation & Code Quality
- 1–2: Produces tests with poor readability, no error handling, frequent flakes.
- 3: Writes clear, well-structured test code with basic logging and assertions.
- 4: Delivers clean, well-tested automation code with robust error handling.
- 5: Produces production-grade code with comprehensive unit tests and clear metrics.
Frameworks & Tooling
- 1–2: Limited awareness of frameworks and poor tool selection decisions.
- 3: Comfortable using primary test frameworks and libraries effectively.
- 4: Configures and extends frameworks to fit product needs and reduces flakiness.
- 5: Evaluates and introduces new tooling that measurably improves test quality or velocity.
CI/CD & Pipeline Integration
- 1–2: Tests are not automated in CI or cause frequent pipeline failures.
- 3: Integrates test suites into CI with sensible run schedules and reporting.
- 4: Optimizes pipeline runs, parallelization, and failure triage to reduce feedback time.
- 5: Designs resilient test pipelines with flaky test mitigation and deployment gating.
Test Strategy & Coverage
- 1–2: Focuses only on UI happy paths with unclear coverage goals.
- 3: Implements clear test cases covering main flows and regression risks.
- 4: Defines risk-based strategies balancing unit, integration, and end-to-end tests.
- 5: Sets measurable coverage goals and drives strategic reduction of risk across releases.
Debugging & Troubleshooting
- 1–2: Struggles to reproduce failures or root cause intermittent errors.
- 3: Can reproduce failures and identify likely causes using logs and traces.
- 4: Remediates root causes, fixes flakiness, and improves observability.
- 5: Anticipates failure modes and builds prevention and rapid diagnosis into pipelines.
Collaboration & Communication
- 1–2: Works in isolation and communicates poorly about test status or failures.
- 3: Shares clear bug reports and coordinates with developers to resolve issues.
- 4: Facilitates cross-functional discussions on testability and release readiness.
- 5: Influences roadmap decisions by articulating test risk and quality trade-offs.
Mentorship & Coaching
- 1–2: Does not share knowledge or help junior engineers improve.
- 3: Provides timely feedback and supports peers on testing practices.
- 4: Actively mentors others and improves team testing capabilities.
- 5: Builds formal learning materials, runs training, and grows team autonomy.
Scoring and weighting
Default weights (adjust per role):
| Dimension | Weight |
|---|---|
| Automation Design | 18% |
| Implementation & Code Quality | 18% |
| Frameworks & Tooling | 14% |
| CI/CD & Pipeline Integration | 14% |
| Test Strategy & Coverage | 12% |
| Debugging & Troubleshooting | 10% |
| Collaboration & Communication | 8% |
| Mentorship & Coaching | 6% |
Final score = weighted average across dimensions. Require at least two “4+” signals for Senior+ roles.
Complete Examples
Senior Test Automation Engineer Scorecard — Great Candidate
| Dimension | Notes | Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Design | Pluggable architecture used across projects | 5 |
| Implementation & Code Quality | Well-covered test modules with CI run-time metrics | 5 |
| Frameworks & Tooling | Built custom plugins or integrated new test tools organization-wide | 5 |
| CI/CD & Pipeline Integration | Parallelized pipelines with automatic rerun and insightful reports | 5 |
| Test Strategy & Coverage | Risk-mapped test plan aligned to release risk | 5 |
| Debugging & Troubleshooting | Implements fixes and adds observability to prevent recurrence | 5 |
| Collaboration & Communication | Leads readiness reviews and risk presentations | 5 |
| Mentorship & Coaching | Runs workshops and establishes team standards | 5 |
Senior Test Automation Engineer Scorecard — Good Candidate
| Dimension | Notes | Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Design | Reusable page objects and helper layers | 3 |
| Implementation & Code Quality | Readable tests with parameterization and retries | 3 |
| Frameworks & Tooling | Works effectively with pytest/JUnit/Selenium/WebDriver | 3 |
| CI/CD & Pipeline Integration | Automated nightly and PR test runs | 3 |
| Test Strategy & Coverage | Balanced suite covering core user journeys | 3 |
| Debugging & Troubleshooting | Finds root cause using logs and stack traces | 3 |
| Collaboration & Communication | Clear reproduction steps and triage notes | 3 |
| Mentorship & Coaching | Regular reviewer and peer helper | 3 |
Senior Test Automation Engineer Scorecard — No-Fit Candidate
| Dimension | Notes | Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Design | Monolithic tests duplicated across suites | 1 |
| Implementation & Code Quality | Hard-coded waits and unclear assertions | 1 |
| Frameworks & Tooling | Only familiar with GUI recorders and no framework experience | 1 |
| CI/CD & Pipeline Integration | Local-only tests not part of CI | 1 |
| Test Strategy & Coverage | Only smoke tests for visible features | 1 |
| Debugging & Troubleshooting | Cannot reproduce flaky failure locally | 1 |
| Collaboration & Communication | Does not provide actionable bug reports | 1 |
| Mentorship & Coaching | No participation in code reviews or onboarding | 1 |
Recruiter FAQs about this scorecard
Q: Do scorecards actually reduce bias?
A: Yes—when you use the same questions, anchored rubrics, and require evidence-based notes.
Q: How many dimensions should we score?
A: Stick to 6–8 core dimensions. More than 10 dilutes signal.
Q: How do we calibrate interviewers?
A: Run monthly sessions with sample candidate answers and compare scores.
Q: How do we handle candidates who spike in one area but are weak elsewhere?
A: Use weighted average but define non-negotiables.
Q: How should we adapt this for Junior vs. Senior roles?
A: Keep dimensions the same but raise expectations for Senior+.
Q: Does this work for take-home or live coding?
A: Yes. Apply the same dimensions, but adjust scoring criteria for context.
Q: Where should results live?
A: Store structured scores and notes in your ATS or ZYTHR.
Q: What if interviewers disagree widely?
A: Require written evidence, reconcile in debrief, or add a follow-up interview.
Q: Can this template be reused for other roles?
A: Yes. Swap technical dimensions for role-specific ones, keep collaboration and communication.
Q: Can ZYTHR auto-populate the scorecard?
A: Yes. ZYTHR can transcribe interviews, tag signals, and live-populate the scorecard.
See Live Scorecards in Action
ZYTHR is not only a resume-screening took, it also automatically transcribes interviews and live-populates scorecards, giving your team a consistent view of every candidate in real time.