Senior DevOps Engineer Interview Scorecard
TL;DR
This scorecard standardizes evaluation of Senior DevOps Engineer candidates by focusing on technical craft, automation, reliability, and cross-team impact. It provides weighted dimensions and concrete behaviors to guide consistent interview ratings and hiring decisions.
Who this scorecard is for
For hiring managers, tech leads, and recruiters evaluating senior-level DevOps candidates. Use this to align interviewers on expectations across architecture, automation, reliability, security, incident response, and collaboration.
Preview the Scorecard
See what the Senior DevOps Engineer Interview Scorecard looks like before you download it.
How to use and calibrate
- Pick the level (Junior, Mid, Senior, or Staff) and adjust anchor examples accordingly.
- Use the quick checklist during the call; fill the rubric within 30 minutes after.
- Or use ZYTHR to transcribe the interview and automatically fill in the scorecard live.
- Run monthly calibration with sample candidate answers to align expectations.
- Average across interviewers; avoid single-signal decisions.
Detailed rubric with anchor behaviors
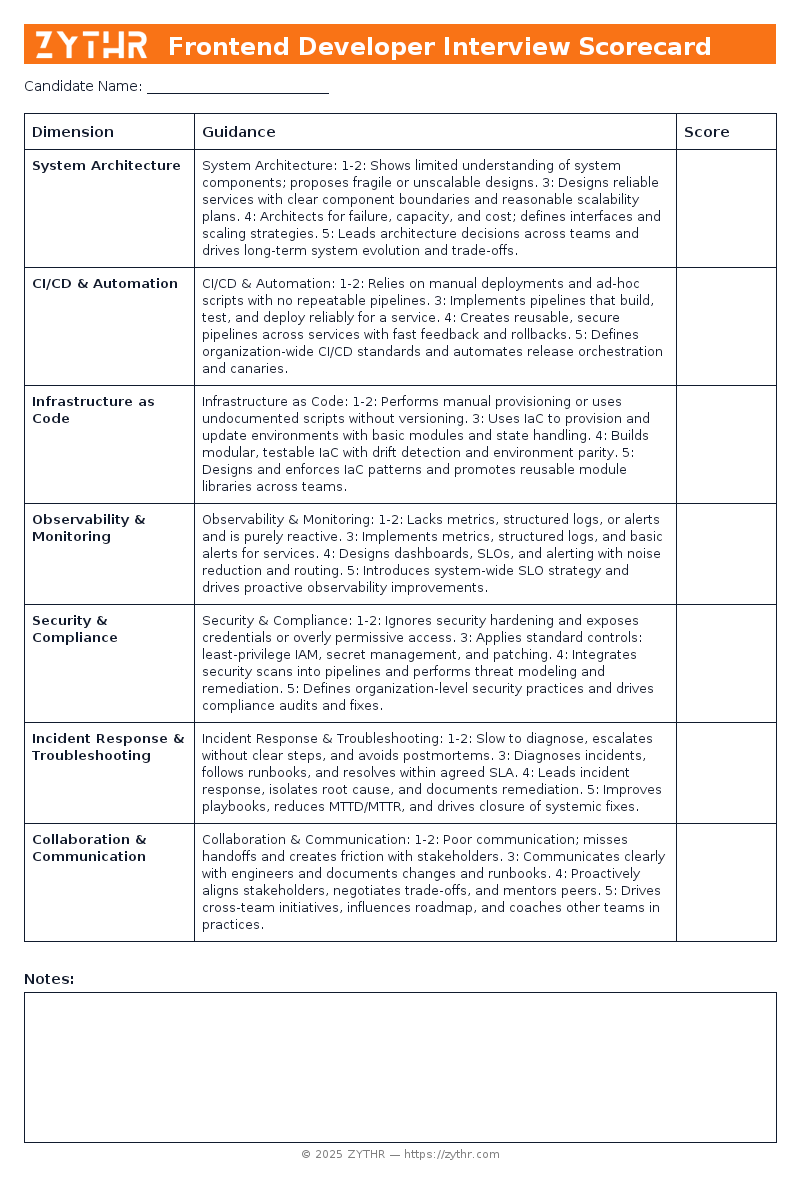
System Architecture
- 1–2: Shows limited understanding of system components; proposes fragile or unscalable designs.
- 3: Designs reliable services with clear component boundaries and reasonable scalability plans.
- 4: Architects for failure, capacity, and cost; defines interfaces and scaling strategies.
- 5: Leads architecture decisions across teams and drives long-term system evolution and trade-offs.
CI/CD & Automation
- 1–2: Relies on manual deployments and ad-hoc scripts with no repeatable pipelines.
- 3: Implements pipelines that build, test, and deploy reliably for a service.
- 4: Creates reusable, secure pipelines across services with fast feedback and rollbacks.
- 5: Defines organization-wide CI/CD standards and automates release orchestration and canaries.
Infrastructure as Code
- 1–2: Performs manual provisioning or uses undocumented scripts without versioning.
- 3: Uses IaC to provision and update environments with basic modules and state handling.
- 4: Builds modular, testable IaC with drift detection and environment parity.
- 5: Designs and enforces IaC patterns and promotes reusable module libraries across teams.
Observability & Monitoring
- 1–2: Lacks metrics, structured logs, or alerts and is purely reactive.
- 3: Implements metrics, structured logs, and basic alerts for services.
- 4: Designs dashboards, SLOs, and alerting with noise reduction and routing.
- 5: Introduces system-wide SLO strategy and drives proactive observability improvements.
Security & Compliance
- 1–2: Ignores security hardening and exposes credentials or overly permissive access.
- 3: Applies standard controls: least-privilege IAM, secret management, and patching.
- 4: Integrates security scans into pipelines and performs threat modeling and remediation.
- 5: Defines organization-level security practices and drives compliance audits and fixes.
Incident Response & Troubleshooting
- 1–2: Slow to diagnose, escalates without clear steps, and avoids postmortems.
- 3: Diagnoses incidents, follows runbooks, and resolves within agreed SLA.
- 4: Leads incident response, isolates root cause, and documents remediation.
- 5: Improves playbooks, reduces MTTD/MTTR, and drives closure of systemic fixes.
Collaboration & Communication
- 1–2: Poor communication; misses handoffs and creates friction with stakeholders.
- 3: Communicates clearly with engineers and documents changes and runbooks.
- 4: Proactively aligns stakeholders, negotiates trade-offs, and mentors peers.
- 5: Drives cross-team initiatives, influences roadmap, and coaches other teams in practices.
Scoring and weighting
Default weights (adjust per role):
| Dimension | Weight |
|---|---|
| System Architecture | 20% |
| CI/CD & Automation | 18% |
| Infrastructure as Code | 15% |
| Observability & Monitoring | 12% |
| Security & Compliance | 12% |
| Incident Response & Troubleshooting | 13% |
| Collaboration & Communication | 10% |
Final score = weighted average across dimensions. Require at least two “4+” signals for Senior+ roles.
Complete Examples
Senior DevOps Engineer Scorecard — Great Candidate
| Dimension | Notes | Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| System Architecture | Defines cross-team architecture with clear trade-offs and migration path. | 5 |
| CI/CD & Automation | Reusable, templated pipelines and automated canary/rollback workflows. | 5 |
| Infrastructure as Code | Reusable module libraries with automated IaC testing and linting. | 5 |
| Observability & Monitoring | SLOs defined, alerting tuned, and runbooks linked to alerts. | 5 |
| Security & Compliance | Automated security scans in CI and documented threat mitigations. | 5 |
| Incident Response & Troubleshooting | Leads postmortem and implements systemic corrective actions. | 5 |
| Collaboration & Communication | Facilitates cross-team planning and mentors junior staff. | 5 |
Senior DevOps Engineer Scorecard — Good Candidate
| Dimension | Notes | Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| System Architecture | Proposes modular services with autoscaling considerations. | 3 |
| CI/CD & Automation | Working pipeline with automated tests and deployments. | 3 |
| Infrastructure as Code | Terraform/CloudFormation modules that manage environments. | 3 |
| Observability & Monitoring | Dashboards and alerts for key service health metrics. | 3 |
| Security & Compliance | Uses managed secret stores and least-privilege roles. | 3 |
| Incident Response & Troubleshooting | Follows runbook and restores service within SLA. | 3 |
| Collaboration & Communication | Writes clear runbooks and informs impacted teams. | 3 |
Senior DevOps Engineer Scorecard — No-Fit Candidate
| Dimension | Notes | Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| System Architecture | Suggests monolithic or single-point-of-failure solutions. | 1 |
| CI/CD & Automation | No pipeline or only manual deployment scripts. | 1 |
| Infrastructure as Code | Manual provisioning or ad-hoc scripts checked into repo. | 1 |
| Observability & Monitoring | No alerts or only ad-hoc logs for debugging. | 1 |
| Security & Compliance | Stores secrets in repos or uses broad IAM roles. | 1 |
| Incident Response & Troubleshooting | Unable to trace alerts to root cause or coordinate response. | 1 |
| Collaboration & Communication | Does not document work or ignores stakeholder input. | 1 |
Recruiter FAQs about this scorecard
Q: Do scorecards actually reduce bias?
A: Yes—when you use the same questions, anchored rubrics, and require evidence-based notes.
Q: How many dimensions should we score?
A: Stick to 6–8 core dimensions. More than 10 dilutes signal.
Q: How do we calibrate interviewers?
A: Run monthly sessions with sample candidate answers and compare scores.
Q: How do we handle candidates who spike in one area but are weak elsewhere?
A: Use weighted average but define non-negotiables.
Q: How should we adapt this for Junior vs. Senior roles?
A: Keep dimensions the same but raise expectations for Senior+.
Q: Does this work for take-home or live coding?
A: Yes. Apply the same dimensions, but adjust scoring criteria for context.
Q: Where should results live?
A: Store structured scores and notes in your ATS or ZYTHR.
Q: What if interviewers disagree widely?
A: Require written evidence, reconcile in debrief, or add a follow-up interview.
Q: Can this template be reused for other roles?
A: Yes. Swap technical dimensions for role-specific ones, keep collaboration and communication.
Q: Can ZYTHR auto-populate the scorecard?
A: Yes. ZYTHR can transcribe interviews, tag signals, and live-populate the scorecard.
See Live Scorecards in Action
ZYTHR is not only a resume-screening took, it also automatically transcribes interviews and live-populates scorecards, giving your team a consistent view of every candidate in real time.