Senior Backend Engineer Interview Scorecard
TL;DR
This scorecard standardizes evaluation of Senior Backend Engineer candidates across core backend craft, reliability, and collaboration. It provides concrete behaviors and signals to help interviewers make consistent, role-aligned hiring decisions.
Who this scorecard is for
Hiring managers, tech leads, and interviewers assessing candidates for Senior Backend Engineer roles. Recruiters and interview panel coordinators can use it to align expectations and frame interview questions.
Preview the Scorecard
See what the Senior Backend Engineer Interview Scorecard looks like before you download it.
How to use and calibrate
- Pick the level (Junior, Mid, Senior, or Staff) and adjust anchor examples accordingly.
- Use the quick checklist during the call; fill the rubric within 30 minutes after.
- Or use ZYTHR to transcribe the interview and automatically fill in the scorecard live.
- Run monthly calibration with sample candidate answers to align expectations.
- Average across interviewers; avoid single-signal decisions.
Detailed rubric with anchor behaviors
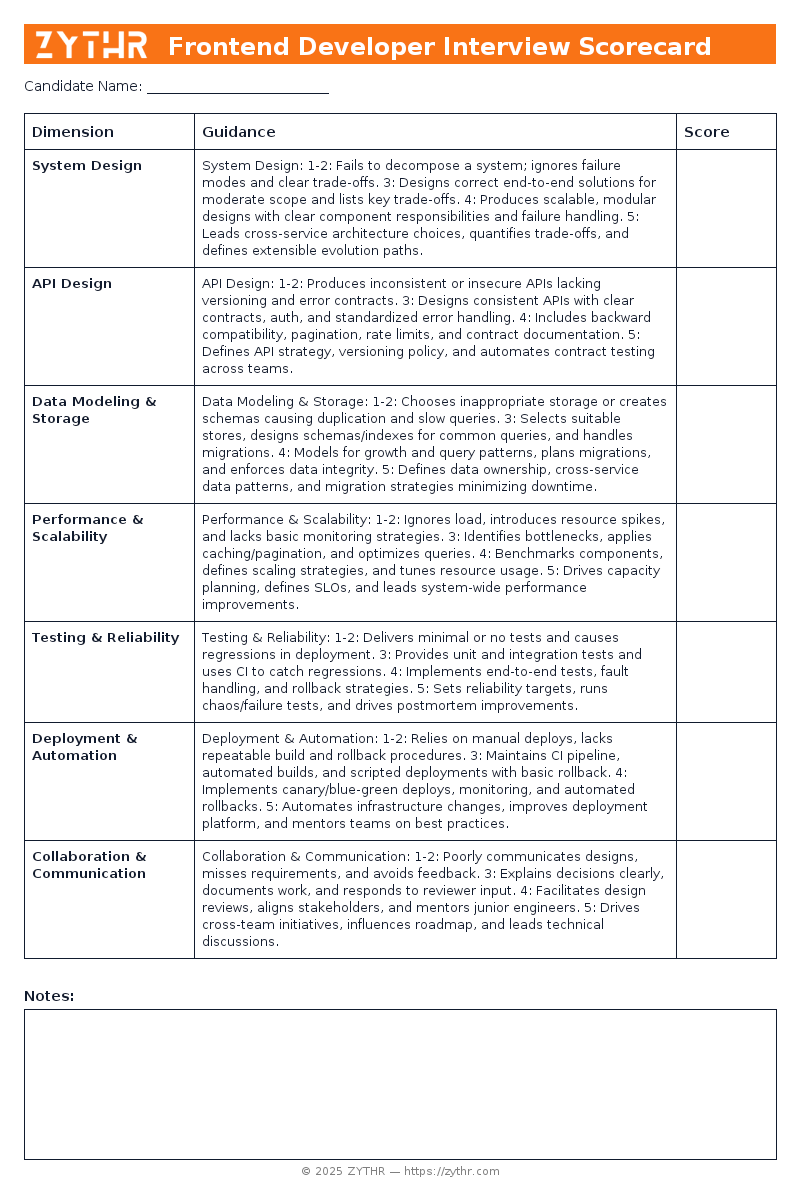
System Design
- 1–2: Fails to decompose a system; ignores failure modes and clear trade-offs.
- 3: Designs correct end-to-end solutions for moderate scope and lists key trade-offs.
- 4: Produces scalable, modular designs with clear component responsibilities and failure handling.
- 5: Leads cross-service architecture choices, quantifies trade-offs, and defines extensible evolution paths.
API Design
- 1–2: Produces inconsistent or insecure APIs lacking versioning and error contracts.
- 3: Designs consistent APIs with clear contracts, auth, and standardized error handling.
- 4: Includes backward compatibility, pagination, rate limits, and contract documentation.
- 5: Defines API strategy, versioning policy, and automates contract testing across teams.
Data Modeling & Storage
- 1–2: Chooses inappropriate storage or creates schemas causing duplication and slow queries.
- 3: Selects suitable stores, designs schemas/indexes for common queries, and handles migrations.
- 4: Models for growth and query patterns, plans migrations, and enforces data integrity.
- 5: Defines data ownership, cross-service data patterns, and migration strategies minimizing downtime.
Performance & Scalability
- 1–2: Ignores load, introduces resource spikes, and lacks basic monitoring strategies.
- 3: Identifies bottlenecks, applies caching/pagination, and optimizes queries.
- 4: Benchmarks components, defines scaling strategies, and tunes resource usage.
- 5: Drives capacity planning, defines SLOs, and leads system-wide performance improvements.
Testing & Reliability
- 1–2: Delivers minimal or no tests and causes regressions in deployment.
- 3: Provides unit and integration tests and uses CI to catch regressions.
- 4: Implements end-to-end tests, fault handling, and rollback strategies.
- 5: Sets reliability targets, runs chaos/failure tests, and drives postmortem improvements.
Deployment & Automation
- 1–2: Relies on manual deploys, lacks repeatable build and rollback procedures.
- 3: Maintains CI pipeline, automated builds, and scripted deployments with basic rollback.
- 4: Implements canary/blue-green deploys, monitoring, and automated rollbacks.
- 5: Automates infrastructure changes, improves deployment platform, and mentors teams on best practices.
Collaboration & Communication
- 1–2: Poorly communicates designs, misses requirements, and avoids feedback.
- 3: Explains decisions clearly, documents work, and responds to reviewer input.
- 4: Facilitates design reviews, aligns stakeholders, and mentors junior engineers.
- 5: Drives cross-team initiatives, influences roadmap, and leads technical discussions.
Scoring and weighting
Default weights (adjust per role):
| Dimension | Weight |
|---|---|
| System Design | 20% |
| API Design | 15% |
| Data Modeling & Storage | 15% |
| Performance & Scalability | 15% |
| Testing & Reliability | 12% |
| Deployment & Automation | 13% |
| Collaboration & Communication | 10% |
Final score = weighted average across dimensions. Require at least two “4+” signals for Senior+ roles.
Complete Examples
Senior Backend Engineer Scorecard — Great Candidate
| Dimension | Notes | Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| System Design | componentized architecture with roadmap and metrics | 5 |
| API Design | stable versioned APIs with automated contract tests | 5 |
| Data Modeling & Storage | migration plan and cross-service data ownership defined | 5 |
| Performance & Scalability | capacity plan with SLOs and optimization roadmap | 5 |
| Testing & Reliability | end-to-end and fault-injection tests with runbook | 5 |
| Deployment & Automation | canary deploys with automated rollback and infra automation | 5 |
| Collaboration & Communication | led cross-team design and mentored others | 5 |
Senior Backend Engineer Scorecard — Good Candidate
| Dimension | Notes | Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| System Design | clear end-to-end design with trade-offs noted | 3 |
| API Design | well-documented endpoints with auth and errors | 3 |
| Data Modeling & Storage | schema and indexes aligned to query patterns | 3 |
| Performance & Scalability | identifies bottlenecks and applies caching | 3 |
| Testing & Reliability | unit and integration tests in CI | 3 |
| Deployment & Automation | CI-driven builds and scripted deploys | 3 |
| Collaboration & Communication | clear design write-ups and receptive to feedback | 3 |
Senior Backend Engineer Scorecard — No-Fit Candidate
| Dimension | Notes | Score (1–5) |
|---|---|---|
| System Design | monolithic design ignoring scaling and failures | 1 |
| API Design | inconsistent endpoints and missing error handling | 1 |
| Data Modeling & Storage | poor schema causing heavy joins and slow behavior | 1 |
| Performance & Scalability | no plan for load or monitoring | 1 |
| Testing & Reliability | no automated tests or flaky CI | 1 |
| Deployment & Automation | manual deploys and fragile rollbacks | 1 |
| Collaboration & Communication | misses requirements and ignores reviewers | 1 |
Recruiter FAQs about this scorecard
Q: Do scorecards actually reduce bias?
A: Yes—when you use the same questions, anchored rubrics, and require evidence-based notes.
Q: How many dimensions should we score?
A: Stick to 6–8 core dimensions. More than 10 dilutes signal.
Q: How do we calibrate interviewers?
A: Run monthly sessions with sample candidate answers and compare scores.
Q: How do we handle candidates who spike in one area but are weak elsewhere?
A: Use weighted average but define non-negotiables.
Q: How should we adapt this for Junior vs. Senior roles?
A: Keep dimensions the same but raise expectations for Senior+.
Q: Does this work for take-home or live coding?
A: Yes. Apply the same dimensions, but adjust scoring criteria for context.
Q: Where should results live?
A: Store structured scores and notes in your ATS or ZYTHR.
Q: What if interviewers disagree widely?
A: Require written evidence, reconcile in debrief, or add a follow-up interview.
Q: Can this template be reused for other roles?
A: Yes. Swap technical dimensions for role-specific ones, keep collaboration and communication.
Q: Can ZYTHR auto-populate the scorecard?
A: Yes. ZYTHR can transcribe interviews, tag signals, and live-populate the scorecard.
See Live Scorecards in Action
ZYTHR is not only a resume-screening took, it also automatically transcribes interviews and live-populates scorecards, giving your team a consistent view of every candidate in real time.